Occipital Neuralgia: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Healing Cycle & Treatment
Occipital Neuralgia: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Healing Cycle & Treatment

Introduction
Occipital neuralgia pain arises due to the pathophysiology of the third occipital nerve, lesser occipital nerve, and greater occipital nerve along the anatomic course of these nerves. This distinct type of headache is accompanied by chronic pain in the back of the head, upper neck, and area posterior to the ears. Pain in the neck region may radiate to the cranium. Subsequent sections of this article describe the causes, risk factors, and treatment of occipital neuralgia.
What is Occipital Neuralgia?
Occipital neuralgia is a paroxysmal painful condition that involves the distribution of either or all the three nerves.
- Lesser occipital nerve
- Greater occipital nerve
- Third occipital nerve
This lancinating pain may last from seconds to minutes and arises due to pathologies of the above-mentioned nerves. The mean age of occipital neuralgia diagnosis is 54.1 years and it is involved in approximately 8.3% of the total facial pain cases. [1]
Symptoms of Occipital Neuralgia
Following are the clinical features of occipital neuralgia. [2]
- Stabbing or shooting pain in the neck region that may radiate to the cranium.
- The persistent and paroxysmal pain may be perceived in the retro-orbital region.
- Cervical sympathicus
- Ocular pain
- Vision impairment
- Vertiges
- Tinnitus
- Nausée
- Congestion of the nasal cavity
- Hypoesthesia or dysesthesia
- Pain in the occipital region may be unilateral or bilateral and can radiate to the vertex of the scalp
- Tenderness during physical examination along the pathway of the lesser occipital nerve and greater occipital nerve
Causes and Risk Factors of Occipital Neuralgia
Approximately 90% of the total occipital neuralgia is attributed to the pathophysiology of the greater occipital nerve. The remaining 10% of the cases are caused by the pathophysiology of the lesser occipital nerve. The primary nerve pathophysiology involves herpes zoster infection and demyelinating lesions. Compression of the lesser occipital nerve, greater occipital nerve, and third occipital nerve at different anatomic sites in the course of these nerves leads to the onset of occipital neuralgia. [1]
Other causes and risk factors of occipital neuralgia include the following.
- Poor posture while driving and/or working on a computer
- Whiplash injury
- Intervertebral disc herniation
- Arthrose
- Contraction musculaire
- Muscle strains due to poor posture
- Other diseases including gout and diabetes mellitus
Cycle de guérison normal
Prior to the discussion about the treatment of occipital neuralgia, it is imperative to discuss the normal healing cycle. The three key stages of the healing cycle include inflammation, proliferation, and maturation. Each stage is described in the subsequent sections. [3]
Stade inflammatoire
The cardinal signs of inflammation include redness, pain, warmth, swelling, and loss of function in the affected area. During the inflammation stage, the activation of the immune response eradicates the disease-causing pathogens.
Stade de prolifération
The proliferation stage of the healing cycle is characterized by the formation of scar tissue in the wound defect. During the proliferation stage, proliferating fibroblasts lay down collagen along with the formation of new blood vessels, synthesis of extracellular matrix, and production of granulation tissue. Excessive formation of scar tissue during this stage leads to the formation of myofascial trigger points and fascia restrictions.
Stade de Maturation
During the maturation stage, resolution of the healing cycle and formation of the wound takes place. Completion of the maturation stage of the healing cycle reflects the elimination of the disease-causing pathogen or other agents. During this stage, the products including cells and chemical mediators are also cleared off from the affected site.
During the onset of chronic inflammation, which lasts for a relatively longer duration than acute inflammation, the affected tissue oscillates between the inflammatory and proliferative phases of the healing cycle. Failure of the healing cycle to commence to the maturation or resolution stage is the key characteristic of chronic inflammation.
Ineffective Treatments of Occipital Neuralgia
Individuals suffering from occipital neuralgia may opt for the following home remedies in order to alleviate the symptoms of this disease. The following remedies only provide short-term relief and some of the remedies may even aggravate the inflammation and proliferation processes of the healing cycle.
- Massage thérapeutique
- Massage therapy using the foam roller
- Application of heat and ice therapy
- Stimulation électrique de la zone touchée
- Strength exercises during the inflammatory phase of the healing cycle
- Élongation
Effective Treatments of Occipital Neuralgia
Effective treatment of occipital neuralgia comprises the following strategies.
- Correction of the posture and core stabilization.
- On doit rester actif et participer à des activités sans douleur.
- One shall also perform pain-free neck exercises.
- The resolution of the inflammation stage of the healing cycle comprises the following tools.
- Individuals suffering from occipital neuralgia shall obtain adequate rest for the management of mild inflammation.
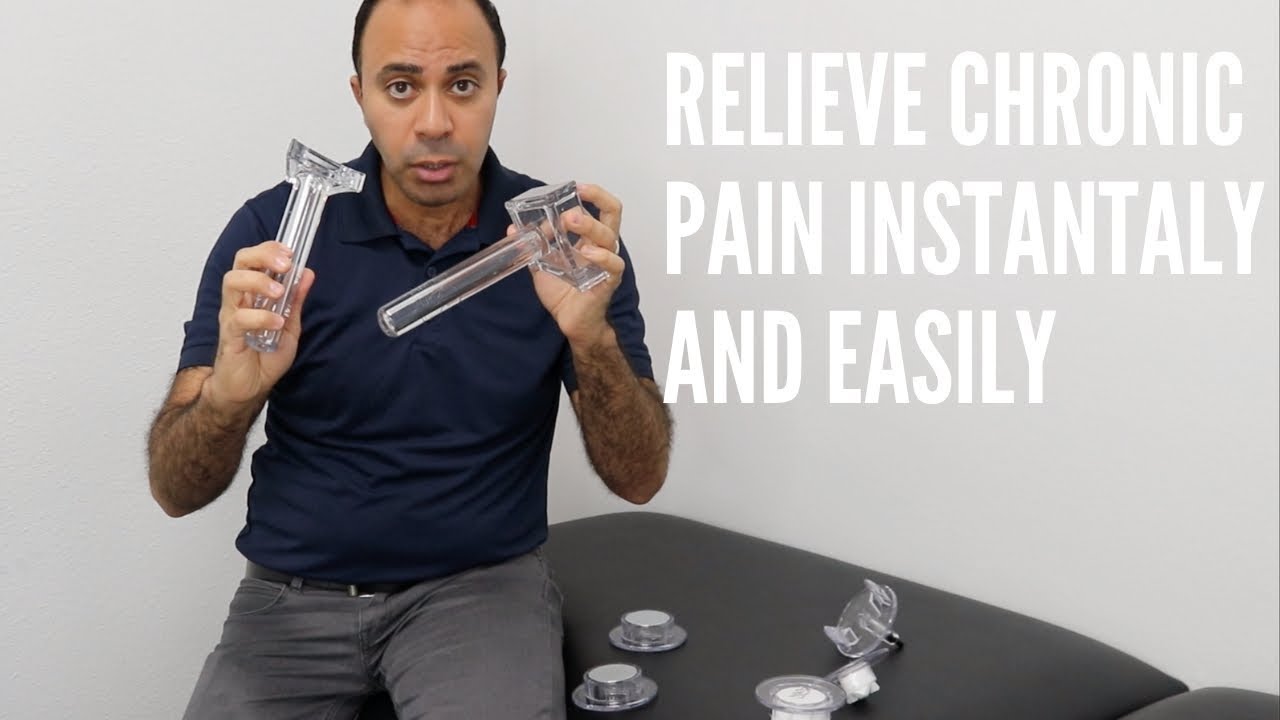
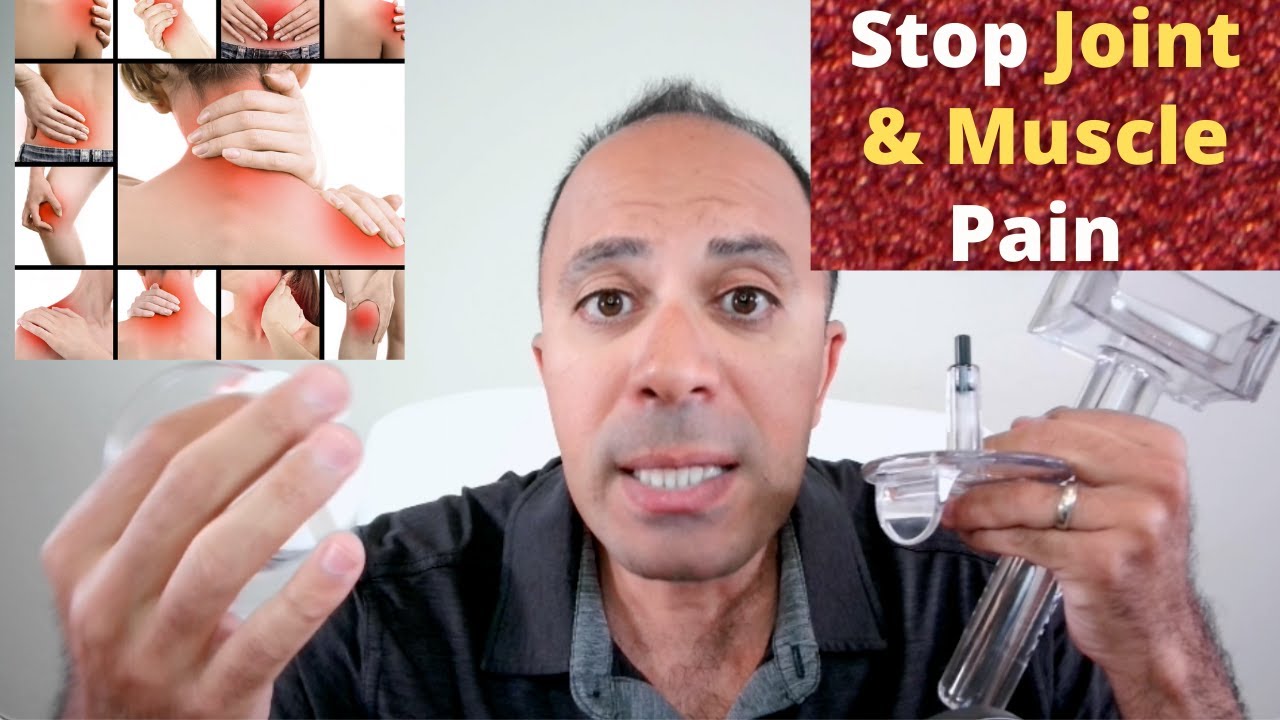
- MagnaHeal device uses magnetic therapy to resolve inflammation. This device is made of a rare earth magnet called neodymium coated with anti-inflammatory substances. The two categories of this device are MagnaHeal 1 and MagnaHeal 2. The magnetic force length of MagnaHeal is approximately 2 inches whereas the magnetic force length of MagnaHeal 2 is 3 inches. While MagnaHeal 1 is beneficial for acute inflammation, chronic inflammation can be resolved using MagnaHeal which provides deeper stimulation. [4]
- Individuals suffering from occipital neuralgia may benefit from the consumption of an anti-inflammatory diet. The diet modulates inflammation and alleviates the symptoms of occipital neuralgia. The components of the anti-inflammatory diet include herbs, spices, monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), fruits, and legumes. [5]
- Individuals must use the AskASTR program to identify nutrient deficiencies and acquire information about nutrient supplementation.
- The resolution of the proliferation stage of the healing cycle comprises the following tools.
- Superficial fascia and aponeurotic fascia restrictions are resolved using the A1 tool.
- Superficial scar tissue and superficial muscle trigger points can be resolved using the A3 tool.
- Deeper muscle trigger points, deeper scar tissue, and fascial restrictions of epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium can be resolved using the A5 tool.
Conclusion
Occipital neuralgia arises due to herpes zoster infection, demyelinating lesions, and compression of nerves along their anatomic course. Individuals suffering from occipital neuralgia may opt for conventional remedies including heat and ice therapy, electrical stimulation, stretching, strengthening of muscles, and massage therapy. Adequate treatment regimens include resolution of the inflammatory and proliferation stages of the healing cycle including MagnaHeal device, anti-inflammatory diet, and A1, A3, and A5 tools.
Références
Occipital Neuralgia Home Treatment

- Résultats rapides
- Le traitement prend environ 5 minutes par jour
- Des outils médicaux faciles à utiliser
- Approche holistique naturelle
- Traiter la cause profonde du problème
- Inventé par un médecin qui souffrait de douleurs chroniques
- Soutenu par plus de 45 études
ASTR exceptionnellement différent
Commentaires recueillis sur divers sites web
- For adult & children
- Soulagement rapide de la douleur
- Réduire l'inflammation
- Soins des plaies
- Ingrédients biologiques et sûrs
- Formulé par le Dr. Jacobs
- Soutenu par des études de recherche