Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Healing Cycle & Treatment
Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Healing Cycle & Treatment

Introducción
Myofascial pain syndrome is a common condition in individuals suffering from musculoskeletal disorders. Pain arises due to disruption in the myofascial system which comprises muscles and associated connective tissue. The following sections discuss the causes, risk factors, clinical features, healing cycle, and treatment of myofascial pain syndrome.
¿Qué es el Síndrome de Dolor Miofascial?
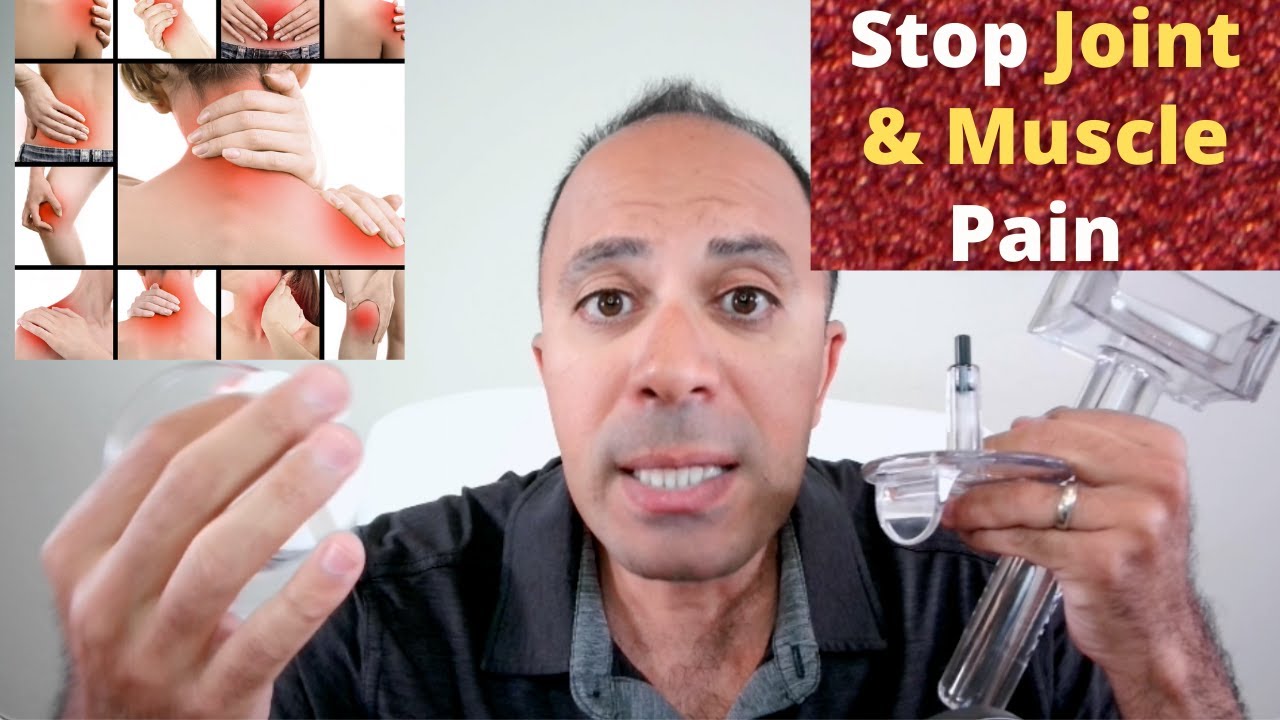
Myofascial pain syndrome refers to pain that arises from muscles and associated fascia layers. This condition is prevalent (30-85%) among individuals suffering from musculoskeletal disorders. The pain may be localized to a certain area or may be referred to other areas as per a pattern. Physical examination also identifies the development of trigger points. Myofascial pain syndrome may have an acute or chronic course. [1]
What is Fascial System?
The fascial system comprises solid components such as muscles, adipose tissue, bone, and cartilage as well as liquid components including blood and lymph. The myofascial system is made up of contractile muscle and corresponding connective tissue. The connective tissue component of the myofascial system is responsible for developing the muscle shape, orienting the neurovasculature, penetrating the muscle, and forming muscle origin and insertion on the bone. The myofascial system also encloses the nerves, vessels, and lymphatics. This system connects different muscles and creates an interconnected network. [2]
The fascia system is divided into superficial and deep components. While superficial fascia is a single entity, the deep fascia is further divided into aponeurotic, epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium layers. [6]
Síntomas del síndrome de dolor miofascial
- Dolor muscular
- Rigidez articular
- Debilidad muscular
- Limited range of movement at the joint
- Nudos musculares dolorosos
- Sleep disturbances
Causas y factores de riesgo
The causes of myofascial pain syndrome include the following. [2]
- The muscular system is exposed to persistent microtrauma which alters the mechano-metabolic environment. This leads to peripheral and central sensitization to pain.
- The development of trigger points occurs due to alterations in the muscle synaptic plate. A higher concentration of acetylcholine leads to constant contraction of muscle fibers, depletion of ATP, and secretion of inflammatory mediators.
- Fibroblasts in the connective tissue transform into myofibroblasts which lead to shortening and increased tone of the surrounding tissue.
- Changes in the properties of hyaluronan and production of a viscous extracellular matrix.
- Altered blood flow causes ischemia in muscles.
Following are the risk factors of myofascial pain syndrome. [1]
- Ergonomic factors
- Abnormal posture
- Overuse activities
- Mala mecánica corporal.
- Traumatic events
- accidente de latigazo
- Lesión por esfuerzo repetitivo
- Structural factors
- Escoliosis
- Osteoartritis
- Spondylosis
- Systemic factors
- Iron deficiency
- hipotiroidismo
- Vitamin D deficiency
Ciclo de curación normal
It is important to understand the normal healing cycle before discussing the treatment and management of myofascial pain syndrome. Acute inflammation is of shorter duration and the healing cycle successfully commences to the resolution stage. In contrast to that, chronic inflammation lasts several months or years. Chronic inflammation is characterized by the simultaneous onset of inflammation and proliferation stages of the healing cycle and the affected site fails to achieve resolution. Following are the stages of the healing cycle. [3]
Etapa de inflamación
Inflammation is the initial stage of the healing cycle. This stage is characterized by the release of cytokines and mediators by the inflammatory cells. In turn, these mediators recruit immune cells to the affected site so as to eliminate the cause of inflammation. A clean wound site marks the completion of the inflammation stage. The characteristics features of this stage are loss of function, swelling, redness, warmth, and pain.
Etapa de proliferación
This is the second stage of the healing cycle and is characterized by the deposition of collagen fibers by proliferating fibroblasts, formation of new blood vessels, re-epithelization, and synthesis of extracellular matrix. The proliferation stage is regulated by negative feedback mechanisms which cause suppression of excess scar tissue and collagen formation. Disruptions in this stage of the healing cycle may lead to the formation of trigger points and fascia restrictions with subsequent limitations in the range of movement.
Etapa de maduración
The maturation stage marks the completion of the healing cycle. Wound contraction and scar formation occur during this stage. Type 1 collagen replaces type 3 collagen in the scar tissue. The healing cycle resolves during this stage.
Ineffective Treatments of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
The traditional treatment modalities mentioned may provide temporary pain relief, however, these do not influence the inflammation and proliferation stages of the healing cycle.
- Application of ice and heat therapy
- estimulación eléctrica
- Massage therapy with a foam roller
- Terapia de Masajes
- Extensión
- Ejercicios de fuerza durante la etapa de inflamación
Effective Treatments of Myofascial Pain Syndrome
- One must maintain a correct posture.
- One must ensure proper body mechanics.
- One must refer to the following steps for promoting the resolution of the inflammation stage.
- One must take adequate rest to accelerate healing.
- Anti-inflammatory plays a significant role in the resolution of the inflammation stage of the healing cycle. One must avoid the consumption of refined carbohydrates, alcohol, and trans fat which may exacerbate inflammation. The components of an anti-inflammatory diet include fruits, legumes, ginger, green tea, black pepper, and turmeric. [4]
- The MagnaHeal device works on the principles of magnetic therapy to resolve inflammation. A device is made of neodymium which is a rare magnet and coated with anti-inflammatory substances. The magnetic force length of MagnaHeal 1 is 2 inches and is beneficial for mild inflammation. On the contrary, MagnaHeal 2 is beneficial for severe inflammation and has a magnetic force length of 3 inches. [5]
- The AskASTR program is designed to identify nutrient deficiencies and aid individuals in selecting the suitable nutrient supplement to eliminate the deficiency.
- One must refer to the following steps for promoting the resolution of the proliferation stage. [6]
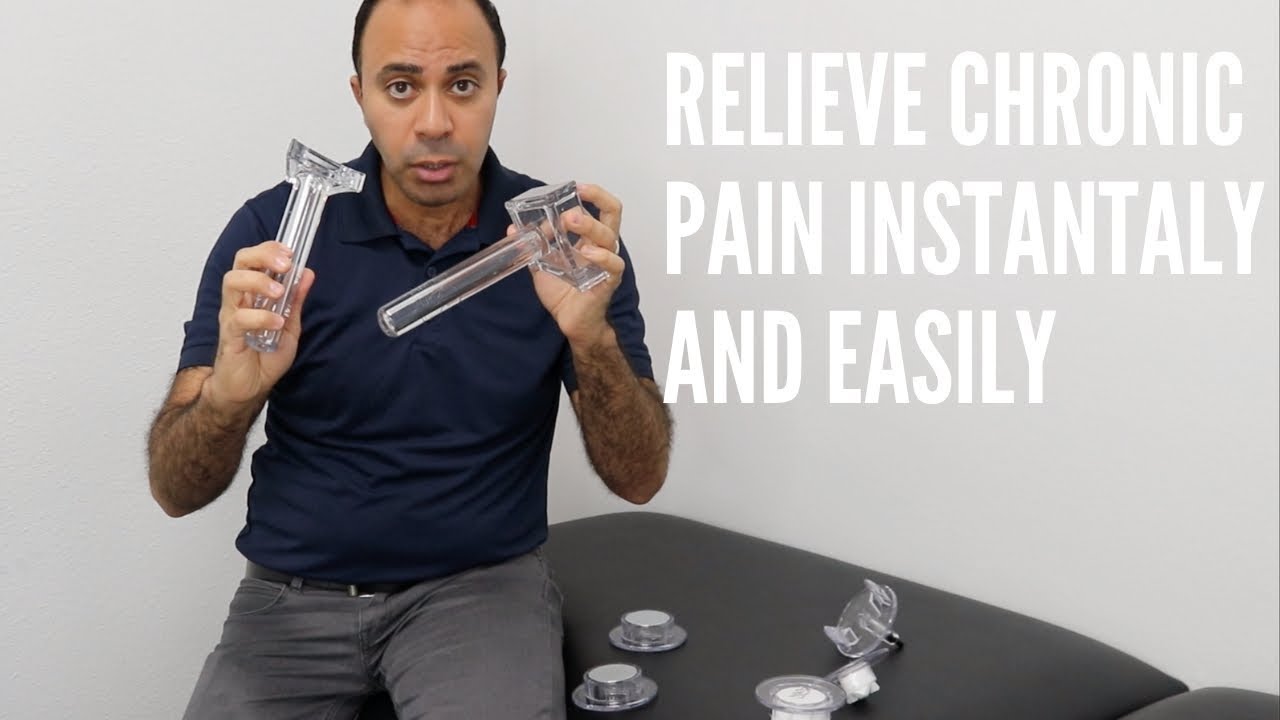
- A1 tool is used for releasing the aponeurotic and superficial fascia restrictions.
- A3 tool is used for releasing muscle trigger points and superficial scar tissue.
- A5 tool is used for releasing trigger points and deep scar tissue. It is also used for releasing epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium fascia restrictions.
Conclusión
The symptoms of myofascial pain syndrome can be improved using the right tools and techniques. Consumption of an anti-inflammatory diet, correction of underlying nutrient deficiencies, and using the MagnaHeal device can help resolve inflammation. Similarly, using A1, A3, and A5 tools can be beneficial for releasing scar tissue, trigger points, and fascia restrictions.
Referencias
Síndrome de dolor miofascial tratamiento en el hogar

- Resultados rápidos
- El tratamiento dura unos 5 minutos al día
- Herramientas médicas fáciles de usar
- Enfoque holístico natural
- Tratar la raíz del problema
- Inventado por un médico que tenía dolor crónico
- Apoyado por más de 45 estudios
ASTR excepcionalmente diferente
Reseñas recopiladas de varios sitios web
- For adult & children
- Alivio rápido del dolor
- Reducir la inflamación
- Cuidado de las heridas
- Ingredientes ecológicos y seguros
- Formulado por el Dr. Jacobs
- Apoyado por estudios de investigación