Peroneal Tendonitis: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Healing Cycle & Treatment
Peroneal Tendonitis: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Healing Cycle & Treatment

序章
Peroneal tendonitis is among the primary three peroneal tendon disorders, characterized by inflammation of the peroneal tendon. This condition presents with lateral and hindfoot pain accompanied by swelling at the ankle. The article discusses the causes, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment of peroneal tendonitis.
What is Peroneal Tendonitis?
The peroneal tendon is located in the lateral compartment of the leg and comprises the peroneus brevis and peroneus longus muscles. Both the muscles derive blood from the peroneal artery and are innervated by the superficial peroneal nerve. The common synovial sheath containing the peroneal tendons is posterior to the distal fibula. After crossing the fibula, the tendons acquire synovial sheath of their own. At the level of the ankle joint, the peroneal tendon is related to the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis anterior muscles. The disorders of the peroneal tendon include peroneal tendonitis, peroneal tendon tears, and peroneal subluxation. These disorders lead to lateral and hindfoot pain. Peroneal tendon disorders are common in young and active individuals. [1]
Symptoms of Peroneal Tendonitis
The symptoms of peroneal tendonitis are as follows. [1, 2]
- Pain at the back of the ankle or hindfoot pain
- Pain when bearing weight
- Swelling at the ankle
- Lateral ankle instability
- Thickening of the peroneal tendon
- Lateral malleolus popping or snapping
- Palpable fluid in the tendon sheath
- Peroneal tendon tenderness in relation to the distal fibula
原因と危険因子
The etiology of peroneal tendonitis is usually multifactorial and arises as a result of extrinsic and intrinsic factors that are mentioned below. [3]
- Inappropriate shoes that offer inadequate support
- Cavus foot or high foot arch
- Improper training techniques
- Activities such as excessive running, jumping and walking
- Sports-related injuries
- Greater and spontaneous mechanical load
- Systemic inflammatory disorders
- 筋肉の緊張
- Inadequate protective gear during training
- Anatomic factors responsible for peroneal tendonitis
- 筋力低下
- Muscle imbalance
- Inflexibility
- Malalignment
- Eccentric contraction of the muscle or forced lengthening
- 肥満
- 喫煙
- Diabetes mellitus
通常の治癒サイクル
To understand the pathogenesis and treatment of peroneal tendonitis, it is important to gain basic knowledge about the normal healing cycle. c healing cycle comprises inflammation, proliferation, and maturation stages. Inflammation can be categorized into acute and chronic inflammation. Acute inflammation is characterized by the resolution of the healing cycle and is of a relatively shorter duration. On the contrary, chronic inflammation is characterized by persistent inflammation and proliferation stages of the healing cycle. During chronic inflammation, the healing cycle fails to attain resolution. [4]
炎症段階
The healing cycle commences with the inflammation stage. The cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, warmth, loss of function, redness, and swelling. During the inflammation stage, the inflammatory cells release cytokines and inflammatory mediators, which then recruit the immune cells. The resolution of the inflammation stage of the healing cycle is characterized by the elimination of the causative agent.
増殖段階
The inflammation stage progresses to the proliferation stage of the healing cycle. This stage is characterized by the formation of newer blood vessels, production of extracellular matrix, the proliferation of fibroblasts and deposition of collagen, and re-epithelization of the wound site. Negative feedback mechanisms are responsible for the regulation of the proliferation stage of the healing cycle. This inhibits the formation of excess scar tissue and the deposition of collagen by fibroblasts. Abnormal progression of the proliferation stage results in the occurrence of fascia restrictions and trigger points which may elicit pain and restrict the range of motion.
成熟段階
The maturation stage is characterized by the resolution of the healing cycle. During this stage of the healing cycle, wound contraction and scar formation occur. Type 3 collagen in the scar tissue is replaced by the formation of type 1 collagen. During chronic inflammation, the healing cycle does not progress through the maturation stage.
Ineffective Treatments of Peroneal Tendonitis
People often opt for traditional and inappropriate treatment techniques for the management of pain and swelling. However, these techniques don’t cater to the underlying abnormalities and only provide temporary pain relief. The ineffective treatments of peroneal tendonitis are listed below.
- マッサージ療法
- Massage therapy using a foam roller
- Use of heat and ice therapy
- 患部の電気刺激
- Mobilization of the ankle joint
- Stretching of the affected area
- 治癒サイクルの炎症段階での筋力トレーニング
Effective Treatments of Peroneal Tendonitis
Appropriate treatment techniques for peroneal tendonitis are as follows.
- Performing daily, occupational, and sports-related activities with a normal gait.
- Wearing good shoes to maintain ankle stability.
- Correct pronation of the foot.
- Resolution of the inflammation stage of the healing cycle.
- An individual must take enough rest to relieve pain and accelerate healing.
- The MagnaHeal device is composed of a rare magnet called neodymium coated with anti-inflammatory substances. The device uses magnetic therapy to modulate inflammation. MagnaHeal 1 has a magnetic force length of 2 inches and MagnaHeal has a magnetic force length of 3 inches beneficial for mild and severe inflammation respectively. [5]
- An individual must consume an anti-inflammatory diet that comprises plant-based products and herbs such as fruits, turmeric, black pepper, green tea, legumes, and ginger. An individual must refrain from alcohol, trans fat, and refined carbohydrates. [6]
- Nutrient deficiencies also play a pivotal role in the onset of inflammation. The AskASTR program is curated to identify nutrient deficiencies using a self-assessment survey.
- Resolution of the proliferation stage of the healing cycle. [7]
- Resolution of this phase involves the release of fascia restrictions, scar tissue, and trigger points. The fascia is divided into the superficial and deep fascia. Deep fascia is further divided into aponeurotic, epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium layers.
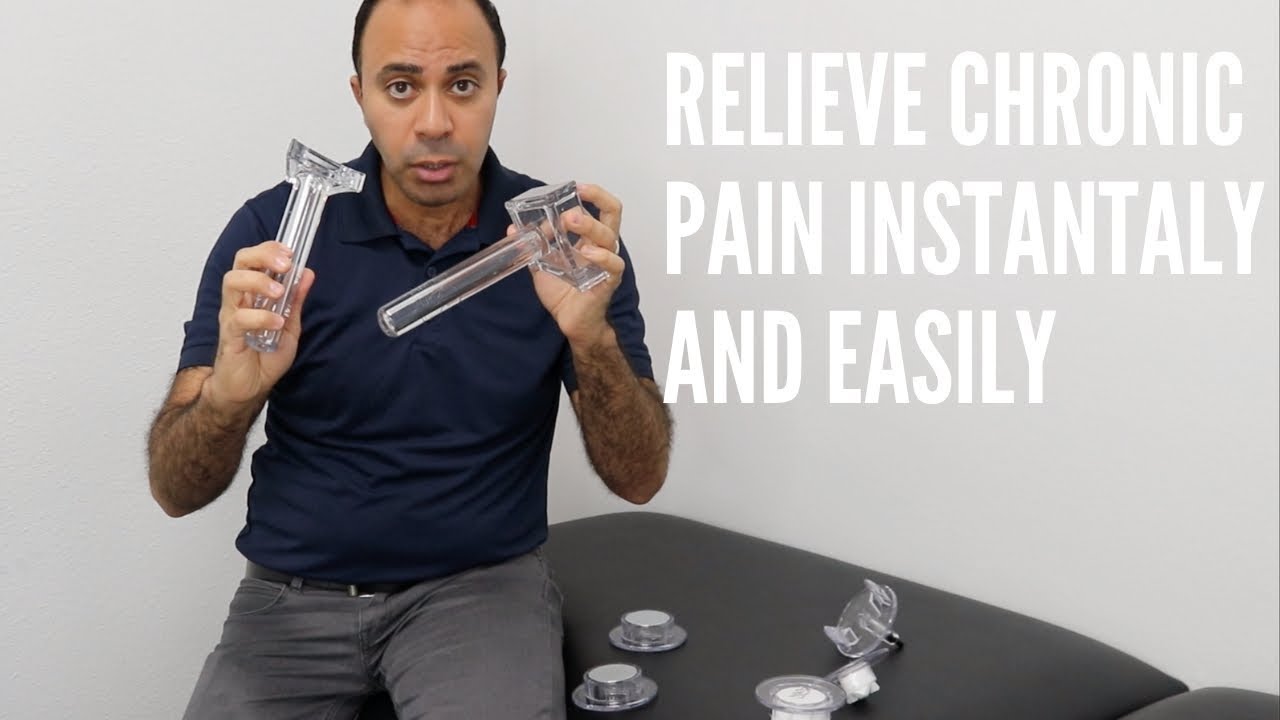
- Release of superficial and aponeurotic fascia restrictions requires the A1 tool.
- Release of superficial scar tissue and trigger points requires the A3 tool.
- Release of deep scar tissue, trigger points, and remaining fascia layers requires the A5 tool.
結論
Peroneal tendonitis occurs due to intrinsic anatomic abnormalities and extrinsic factors such as trauma, improper training techniques, and repetitive movements. This condition limits movement and elicits pain and swelling at the ankle. Appropriate treatment and management of peroneal tendonitis include an anti-inflammatory diet, nutrient supplements, the MagnaHeal device, and the use of A1, A3, and A5 tools.
参考文献
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544354/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5508858/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29078821/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518964/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3617815/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28350517/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526038/
Peroneal Tendonitis Home Treatment

- 速い結果
- 治療は1日約5分かかります
- 使いやすい医療ツール
- 自然な全体論的アプローチ
- 問題の根本原因を処理する
- 慢性的な痛みを持っていた医師によって発明されました
- 45以上の研究によってサポートされています
ASTRは非常に異なる
さまざまなウェブサイトから収集されたレビュー
- For adult & children
- 速い痛みの軽減
- 炎症を減らす
- 創傷ケア
- 有機的で安全な成分
- ジェイコブス博士による処方
- 調査研究によるサポート