Cervical Radiculopathy: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Healing Cycle & Treatment
Cervical Radiculopathy: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Healing Cycle & Treatment

Introduction
Compression of cervical nerve roots gives rise to the onset of cervical radiculopathy. Genetic predisposition, age-related degenerative changes, and disc herniation are the key etiological factors of cervical radiculopathy. The following sections of this article describe the treatment and management of cervical radiculopathy in the background of the normal healing cycle.
What is Cervical Radiculopathy?
Cervical radiculopathy is a condition that arises due to cervical nerve root compression. The clinical manifestations of this condition include motor deficits, pain, sensory deficits, and diminished reflexes. The dysfunction of nerve roots originating from the cervical spinal cord may occur due to different pathological processes. The onset of cervical radiculopathy usually occurs in individuals who are in their 40s and 50s. The annual incidence is 63.5 per 100,000 women and 107.3 per 100,000 men. [1]
Causes and Risk Factors of Cervical Radiculopathy
The characteristic feature of cervical radiculopathy is the compression of nerve roots originating from the cervical spinal cord. Compression leads to nerve injury via chemical and mechanical pathways. Mechanical pathways involve localized ischemia and damage to the nerves. Chemical pathways involve an inflammatory cascade which increases sensitization and pain. The most commonly involved nerve root is C7, followed by C6 and C8 nerve roots. The causes of cervical radiculopathy and associated nerve root compression are listed below. [1]
- Disc herniation
- Bony osteophytes
- Cervical spondylosis
- Foraminal stenosis
- Hypertrophy of the joint
- Genetic factors
- Inflammatory conditions
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
The risk factors for cervical radiculopathy are as follows.
- Cigarette smoking
- Previous lumbar radiculopathy
- White race
- Lifting heavyweights
- Golf
- Frequent diving from pool board
- Vibrating diving equipment
- Trauma or whiplash injury
- Poor posture
- Poor body mechanics for lifting
Symptoms of Cervical Radiculopathy
Cervical radiculopathy usually occurs unilaterally and has the following signs and symptoms. [2]
- Radicular pain
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of sensation
- Tingling or numbness
Normal Healing Cycle
The normal healing cycle is composed of three stages – inflammation, proliferation, and maturation. Before discussing the treatment and management of cervical radiculopathy, one must acquire adequate knowledge about the underlying mechanisms of injury and the normal healing cycle. Each stage of the healing cycle is described as follows.
Inflammation Stage
This is the initial stage of the healing cycle, during which inflammatory cells release inflammatory mediators and cytokines in response to injurious stimuli. These inflammatory mediators and signaling molecules recruit immune cells to the site of injury so as to eliminate the cause. Cardinal signs of inflammation include warmth, redness, pain, loss of function, and swelling.
Proliferation Stage
As the inflammation subsides, the healing cycle progresses to the proliferation stage. The proliferation stage is characterized by re-epithelization of the injured site, synthesis of extracellular matrix, development of newer blood vessels, and deposition of collagen by proliferating fibroblasts. The proliferation stage is modulated by negative feedback mechanisms which prevent excessive deposition of collagen and development of scar tissue. Disruption in these regulatory mechanisms leads to the development of trigger points and fascia restrictions.
Maturation Stage
This is the last stage of the healing cycle. The maturation stage marks the resolution of the healing cycle and is characterized by wound contraction and scar formation. Type 1 collagen replaces the type 3 collagen in the scar tissue.
Acute inflammation attributes to inflammation for a shorter duration and resolution of the healing cycle as it progresses to the maturation stage. Whereas chronic inflammation persists for a longer duration, and the healing cycle oscillates between the inflammation and proliferation. The healing cycle fails to achieve resolution. [3]
Ineffective Treatments for Cervical Radiculopathy
The traditional treatment techniques are practiced at home as well as in clinics. Affected individuals and care providers use the following treatment modalities for alleviating symptoms of cervical radiculopathy, however, these only provide short-term relief and some even may aggravate the symptoms.
- Massage therapy
- Massage therapy using a foam roller
- Stretching of the affected area
- Strength exercises during the inflammation stage
- Electrical stimulation of the affected area
- Application of ice and heat therapy
- Mobilization of joints
Effective Treatments for Cervical Radiculopathy
The following are effective therapeutic techniques for the treatment and management of cervical radiculopathy. These include an anti-inflammatory diet, lifestyle modifications, use of magnetic therapy, using supplements for overcoming nutrient deficiencies, and using specified tools for releasing excessive scar tissue and fascia restrictions.
- One must maintain a proper posture.
- Stabilization of the body core.
- One shall stay active and participate in pain-free activities.
- One shall perform pain-free neck exercises.
- One must follow the mentioned steps to promote the resolution of the inflammation stage.
- Adequate rest promotes healing.
- Nutrient deficiencies contribute to the onset and aggravation of the inflammation stage of the healing cycle. The AskASTR program is designed to recognize nutrient deficiencies in an individual using a short survey. The program also recommends supplements that can be used for overcoming nutrient deficiencies.
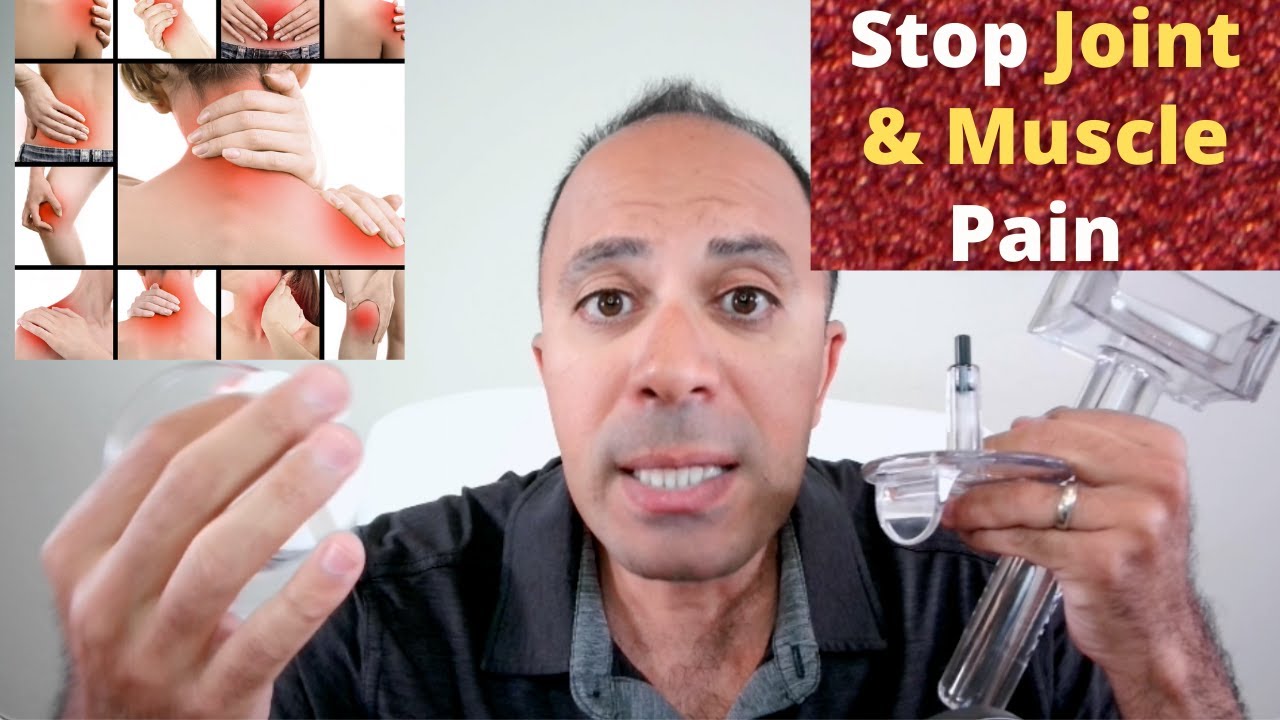
- Magnetic therapy can be employed to modulate inflammation and accelerate healing. The MagnaHeal device is composed of a rare earth magnet, neodymium, which is coated by anti-inflammatory materials. MagnaHeal 1 and MagnaHeal 2 have a magnetic force length of 2 inches and 3 inches respectively. [3]
- Pro-inflammatory foods such as refined carbohydrates and trans fat aggravate inflammation and reduce the rate of healing. On the contrary, anti-inflammatory foods help accelerate healing. These include fruits, legumes, ginger, green tea, turmeric, and black pepper. [4]
- One must follow the mentioned steps to promote the resolution of the proliferation stage. [5]
- A1 tool helps release superficial and aponeurotic fascia restrictions.
- A3 tool helps release trigger points and superficial scar tissue.
- A5 tool helps release trigger points, deep scar tissue, epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium fascia restrictions.
Conclusion
Resolution of the inflammation and proliferation stages of the healing cycle play a pivotal role in the treatment and management of cervical radiculopathy. While adequate rest, an anti-inflammatory diet, and pain-free neck exercises promote healing, additional tools including the MagnaHeal device and A1, A3, and A5 tools also aid in the resolution of inflammation and proliferation stages.
References
Cervical Radiculopathy Home Treatment

- Fast results
- Treatment takes about 5 min a day
- Easy to use medical tools
- Natural holistic approach
- Treat the root cause of the problem
- Invented by a doctor who had chronic pain
- Supported by over 45 studies
ASTR Exceptionally Different
Reviews collected from various websites
- For adult & children
- Fast pain relief
- Reduce Inflammation
- Wound care
- Organic, safe ingredients
- Formulated by Dr. Jacobs
- Supported by research studies